Software Defined Radio Ad Hoc Network
 A 20-node ad hoc network of software-defined radios (SDRs) has been created for testing cooperative transmission (CT) and distributed MIMO (DMIMO) links and routing protocols. Each node consists of a GNU radio and a MICAz node. The GNU radios are used for the experiments with CT and DMIMO, while the MICAz nodes are used only for network telemetry and experiment setup.
A 20-node ad hoc network of software-defined radios (SDRs) has been created for testing cooperative transmission (CT) and distributed MIMO (DMIMO) links and routing protocols. Each node consists of a GNU radio and a MICAz node. The GNU radios are used for the experiments with CT and DMIMO, while the MICAz nodes are used only for network telemetry and experiment setup.
Reaching Farther with Concurrent Cooperative Transmission (CCT)
 A cluster of two or more physically separated radios transmit at the same time to extend the range of radio transmission much beyond the distance a lone, single-antenna radio can reach. CCT range extension is demonstrated experimentally on software-defined radios, using a practical transmit synchronization method for non-coherent FSK.
A cluster of two or more physically separated radios transmit at the same time to extend the range of radio transmission much beyond the distance a lone, single-antenna radio can reach. CCT range extension is demonstrated experimentally on software-defined radios, using a practical transmit synchronization method for non-coherent FSK.
Extending Lifetime of a Multi-Hop Wireless Sensor Network with Cooperative Transmission
 The range extension from CT discussed above can solve the energy hole problem in battery-driven multi-hop wireless sensor networks (WSNs).
The range extension from CT discussed above can solve the energy hole problem in battery-driven multi-hop wireless sensor networks (WSNs).
MAC-Free, Energy-efficient broadcasting in Wireless Networks
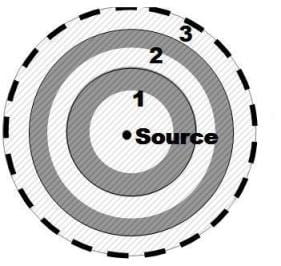 CCT used repeatedly forms a sequence of clusters or Opportunistic Large Arrays (OLAs), where each cluster is defined by which nodes can decode the transmission from the previous cluster. Radios are selected to relay only if their received SNR is lower than a “transmission threshold” to serve as relays. “OLA-T” is the version for mobile networks and “Alternating OLA-T” (A-OLA-T) is appropriate for static networks.
CCT used repeatedly forms a sequence of clusters or Opportunistic Large Arrays (OLAs), where each cluster is defined by which nodes can decode the transmission from the previous cluster. Radios are selected to relay only if their received SNR is lower than a “transmission threshold” to serve as relays. “OLA-T” is the version for mobile networks and “Alternating OLA-T” (A-OLA-T) is appropriate for static networks.
SNR Estimation for Non-coherent FSK
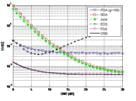 A collection of optimal SNR estimation algorithms are derived for different combinations of pilot and data symbols in the non-coherent FSK recevier. The SNR estimates are used in the OLA-T and A-OLA-T protocols.
A collection of optimal SNR estimation algorithms are derived for different combinations of pilot and data symbols in the non-coherent FSK recevier. The SNR estimates are used in the OLA-T and A-OLA-T protocols.
Concurrent Cooperative Transmission with OFDM
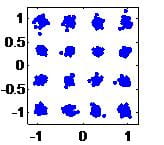 A cluster of two or more physically separated radios transmit OFDM at the same time to extend the range of radio transmission much beyond the distance a lone, single-antenna radio can reach. CCT range extension is demonstrated experimentally on software-defined radios, using a practical transmit synchronization method for OFDM.
A cluster of two or more physically separated radios transmit OFDM at the same time to extend the range of radio transmission much beyond the distance a lone, single-antenna radio can reach. CCT range extension is demonstrated experimentally on software-defined radios, using a practical transmit synchronization method for OFDM.
Methods are employed to reduce the carrier frequency offsets (CFOs), sampling frequency offsets (SFOs), and timing errors, in a cluster transmission.
Concurrent CooperativeTransmission-based Routing for Wireless Sensor Networks
 The CCT broadcast method mentioned above is the first stage of the novel Opportunistic Large Array Concentric Routing Algorithm (OLACRA). In the second stage, CCT is used consecutively to form a sequence of OLAs. No “primary” conventional mult-hop route is needed and the method is MAC-free for a single flow. Therefore, the network overhead is extremely light.
The CCT broadcast method mentioned above is the first stage of the novel Opportunistic Large Array Concentric Routing Algorithm (OLACRA). In the second stage, CCT is used consecutively to form a sequence of OLAs. No “primary” conventional mult-hop route is needed and the method is MAC-free for a single flow. Therefore, the network overhead is extremely light.
Video Transmission Over a Cooperative Route Using Concurrent Cooperative Transmission
 The OLACRA method mentioned above is the basis of the route request and route reply stages of the novel reactive OLA-based routing protocol, called OLAROAD, for ad hoc networks. No “primary” conventional mult-hop route is needed. Because the OLAROAD route is a strip that occupies area, this routing approach is very robust to node mobility
The OLACRA method mentioned above is the basis of the route request and route reply stages of the novel reactive OLA-based routing protocol, called OLAROAD, for ad hoc networks. No “primary” conventional mult-hop route is needed. Because the OLAROAD route is a strip that occupies area, this routing approach is very robust to node mobility
One-Shot Reading of Correlated Sensors Using Semi-Cooperative Spectrum Fusion
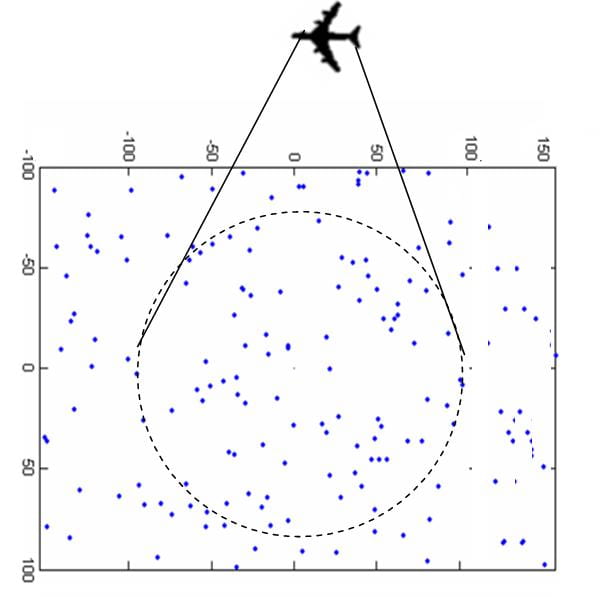 A MAC-free method for obtaining an estimate of the histogram of sensor values within an area that is illuminated by a reader node. The method is shown to consume less energy for comparable estimator performance, when compared to a cluster-based MAC-aided scheme.
A MAC-free method for obtaining an estimate of the histogram of sensor values within an area that is illuminated by a reader node. The method is shown to consume less energy for comparable estimator performance, when compared to a cluster-based MAC-aided scheme.
Exploring Array Reception of the EO-1 Downlink (past project)
 A low-cost adaptive antenna array architecture for low-earth-orbit (LEO) satellite ground stations has been investigated. These ground stations are intended to have no or a minimum of moving parts and could potentially be operated in populated areas, where terrestrial interference is likely. A novel method of synthesizing an array pattern to equalize scanning loss was explored
A low-cost adaptive antenna array architecture for low-earth-orbit (LEO) satellite ground stations has been investigated. These ground stations are intended to have no or a minimum of moving parts and could potentially be operated in populated areas, where terrestrial interference is likely. A novel method of synthesizing an array pattern to equalize scanning loss was explored
Vehicle-to-Vehicle Channel Measurement and Modeling (past project)
Last revised on Jan 28, 2010.

